The teacher-centered learning process has been dominant throughout our educational journey, from our early years to the conclusion of our studies. Traditionally, teachers held the role of primary and indisputable sources of knowledge, and students were expected to follow one universal curriculum.
The learner-centered approach, also known as student-centered learning, inverts this classroom dynamic by putting learners at the center of their learning process and prioritizing their active involvement. It is based on the assumption that there is a natural urge to gain knowledge, especially through experimenting. The approach is often called learning by doing, and many contemporary studies prove that it is way more effective than traditional lectures.
This article explores the principles and benefits of a learner-centered approach and how organizations can use a Learning Management System (LMS) to achieve their goals.
Principles of a learner-centered approach
You might have heard about Maria Montessori, a creator of an educational method known as the Montessori method, which develops kids’ natural interests and abilities. She was a forerunner of student-centered learning that we know today.
A learner-centered approach to education prioritizes the individual student’s needs, interests, and abilities. The core principles of this approach include putting the learner at the center of the learning process, emphasizing active learning, and fostering a collaborative and supportive learning environment. The teacher’s role in a learner-centered approach is to act as a facilitator, guide, and coach rather than simply delivering information.
This approach encourages students to take ownership of their learning and set their own goals, and tailor educational paths to their unique learning style, pace, and needs. Ultimately, a learner-centered approach aims to empower students to become lifelong learners capable of adapting to new challenges in the job market.
Here are the key features of a learner-centered approach:
- Focus on learner needs and interests: In a learner-centered approach, the curriculum and learning activities are designed with students’ needs, interests, and learning styles in mind. This ensures the content is relevant and engaging for them.
- Active participation: Students are not passive recipients of information. They are encouraged to participate actively in their learning process through discussions, problem-solving activities, and asking questions.
- Collaboration: Students are encouraged to work together and learn from each other. Group work and peer-to-peer learning are commonly used in a learner-centered approach.
- Feedback: Regular feedback is provided to students on their progress, strengths, and areas for improvement. Assessment focuses on skill development and understanding rather than learning facts by heart.
Benefits of a learner-centered approach
There are numerous benefits of a learner-centered approach. The most important include:
- Increased motivation: Learners are more motivated to learn when they are actively engaged in learning and feel that their interests and needs are properly addressed.
- Improved knowledge and skill retention: When learners actively engage in the process, they are more likely to remember what they have learned.
- Improved critical thinking: Active participation in the learning process encourages students to think critically, analyze information, and solve problems independently.
- Greater responsibility: Learners take ownership of their learning, which fosters a sense of responsibility for their academic success and developing greater independence and self-reliance.
- Improved communication: Learners can improve their communication skills by working in groups and engaging in discussions and debates.
- Enhanced creativity: A learner-centered approach can foster creativity and innovation, as learners are encouraged to think outside the box and develop their ideas and solutions.
- Better engagement: Learners are more likely to be engaged in the learning process when actively involved, which can lead to better outcomes.
- Lifelong learning skills: A learner-centered approach equips students with essential skills for lifelong learning, allowing them to adapt to a rapidly changing world.
The Challenges
While beneficial for learners, the student-centered approach can present several challenges for teachers and trainers. Catering to diverse learning styles and needs within a student-centered classroom requires more planning and flexibility, as developing engaging activities, projects, and resources takes time and effort. The approach can also present classroom management challenges, particularly when dealing with off-task behavior. Additionally, implementing a student-centered approach can be difficult in large class sizes where individual attention becomes limited.
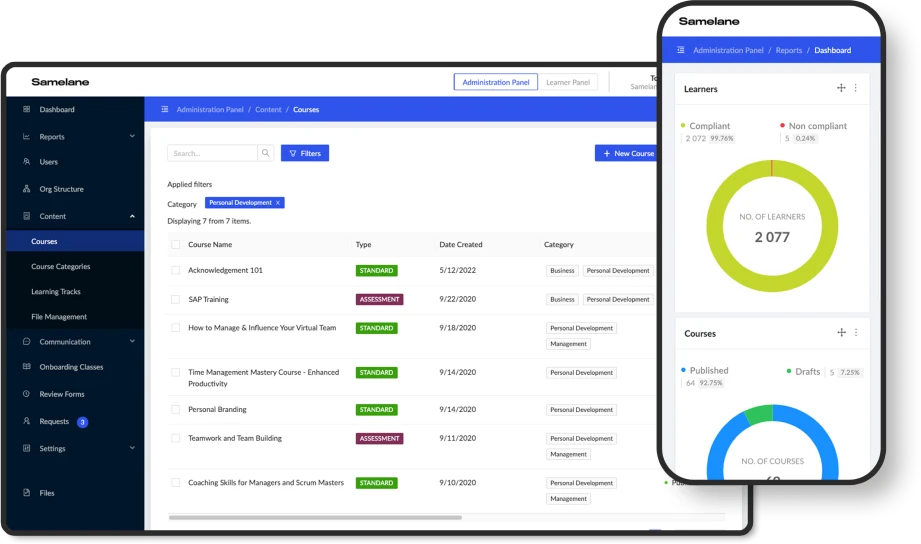
To address these challenges and facilitate a smooth transition to student-centered learning, educational facilities and workplaces increasingly turn to tools that aid this shift. One such tool is Learning Management Systems.
Implementing a learner-centered approach with LMS
Implementing a learner-centered approach with a Learning Management System (LMS) involves designing and delivering learning experiences prioritizing individual learner needs, preferences, and goals.
It delivers all the benefits described in the previous section but in an automated way, freeing up a significant amount of resources and making the learner-centered approach considerably more cost-effective. Additionally, it allows managers to track all learning and development processes in detail, which would never be possible without such a system.
Here are the main features of Learning Management Systems that specifically support the implementation of a learner-centered approach:
- Personalized learning paths: Design custom learning paths tailored to each learner’s needs, goals, and interests. This can include relevant courses, modules, and resources that cater to their unique requirements and skill levels.
- Self-paced learning: Allow learners to progress through the material at their own pace, allowing them to manage their learning according to their schedules and preferences.
- Varied learning formats: Offer a variety of content formats, such as text, audio, video, and interactive simulations, to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
- Interactive and engaging content: Create engaging content that encourages active participation and fosters deep learning. This can include quizzes, games, simulations, and problem-solving exercises.
- Collaborative learning opportunities: Encourage collaboration among learners by incorporating group projects, discussion forums, and peer feedback. This helps to develop communication and teamwork skills while fostering a sense of community.
- Real-world application: Provide opportunities for learners to apply their newly acquired skills and knowledge in real-world situations, such as case studies, virtual labs, or project-based assignments.
- Ongoing feedback and assessment: Implement regular evaluations and feedback mechanisms to help learners track their progress and identify areas for improvement. This can include quizzes, self-assessments, and instructor feedback.
- Accessibility and inclusivity: Ensure that the LMS platform and content are accessible to all learners, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This can involve incorporating assistive technologies, providing alternative content formats, and following accessibility best practices.
- Learner support: Offer comprehensive support to learners throughout their learning journey, including access to instructors, technical assistance, and additional resources.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly gather feedback from learners and analyze their performance data to identify areas for improvement in the LMS experience. Use this information to refine and enhance the learner-centered approach, ensuring it remains effective and relevant.
LMS-aided learner-centered approach
A learner-centered approach is a powerful and effective way to promote engagement, motivation, and knowledge retention in education and training. By prioritizing the needs and interests of learners, organizations can create a more personalized and relevant learning experience that meets learners’ diverse learning styles and preferences. An LMS can be a valuable tool for implementing a learner-centered approach by providing a platform for delivering, tracking, and managing personalized learning experiences. Educators and trainers can help learners achieve their learning goals and thrive in today’s dynamic and ever-changing world by adopting a learner-centered approach and leveraging the power of an LMS.