Traditional learning methods, typically characterized by a structured, linear approach focused on standardized testing and uniform curriculums, have been the mainstay in educational and professional settings. However, in our rapidly evolving and interconnected world, these methods show their limitations. Enter agile learning, a flexible and iterative approach to education that prioritizes adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
Agile learning is specifically designed to meet the changing needs of learners in a dynamic environment. Its growing importance stems from its ability to quickly equip individuals with the skills to adapt to new information and circumstances, making it highly relevant in today’s fast-paced world.
This article is dedicated to guiding readers through the transition from the traditional, rigid learning frameworks to the more adaptable and responsive world of agile learning, outlining the steps, benefits, and challenges of this transformative journey.
Understanding Conventional Learning
Conventional learning methodologies have been fundamental to education systems and professional training programs for decades. These methodologies are often characterized by a teacher-centered approach, where instruction is primarily one-way, from teacher to student, and learning is usually evaluated through standardized tests and assessments.
The main advantages of traditional learning include a structured environment, clear expectations, and a focused curriculum, which can provide a solid foundation of knowledge. However, the limitations of this approach are becoming increasingly evident, especially in our rapidly changing world.
Traditional learning can be rigid, limiting creativity and critical thinking, and may only sometimes cater to the diverse needs of all learners. Furthermore, it often needs to adequately prepare students for the realities of the modern workforce, which demands adaptability, problem-solving skills, and lifelong learning.
Recognizing these shortcomings highlights the urgent need for change in the educational and professional landscape, paving the way for more dynamic and responsive learning models like agile learning.
Introducing Agile Methodology
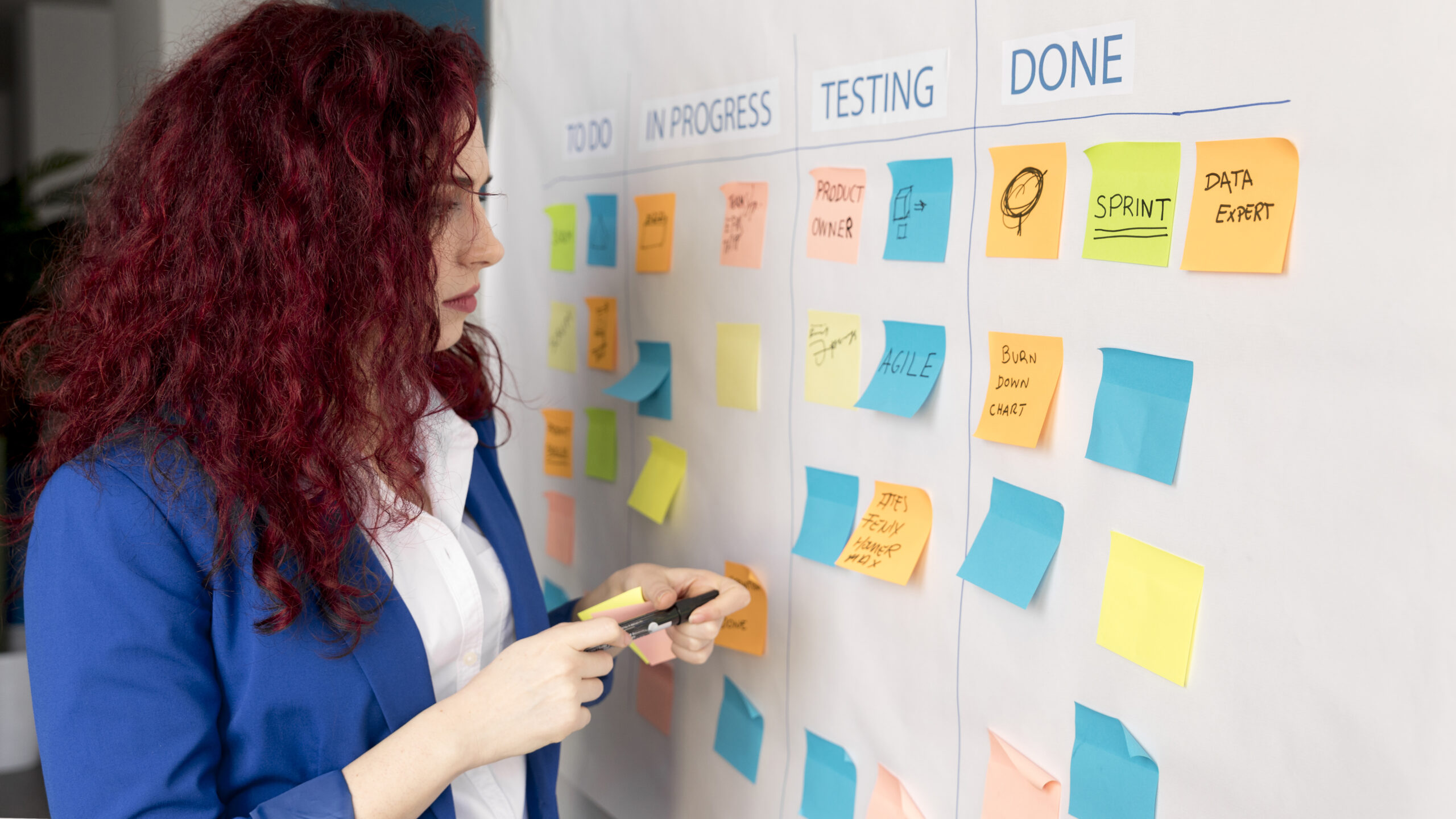
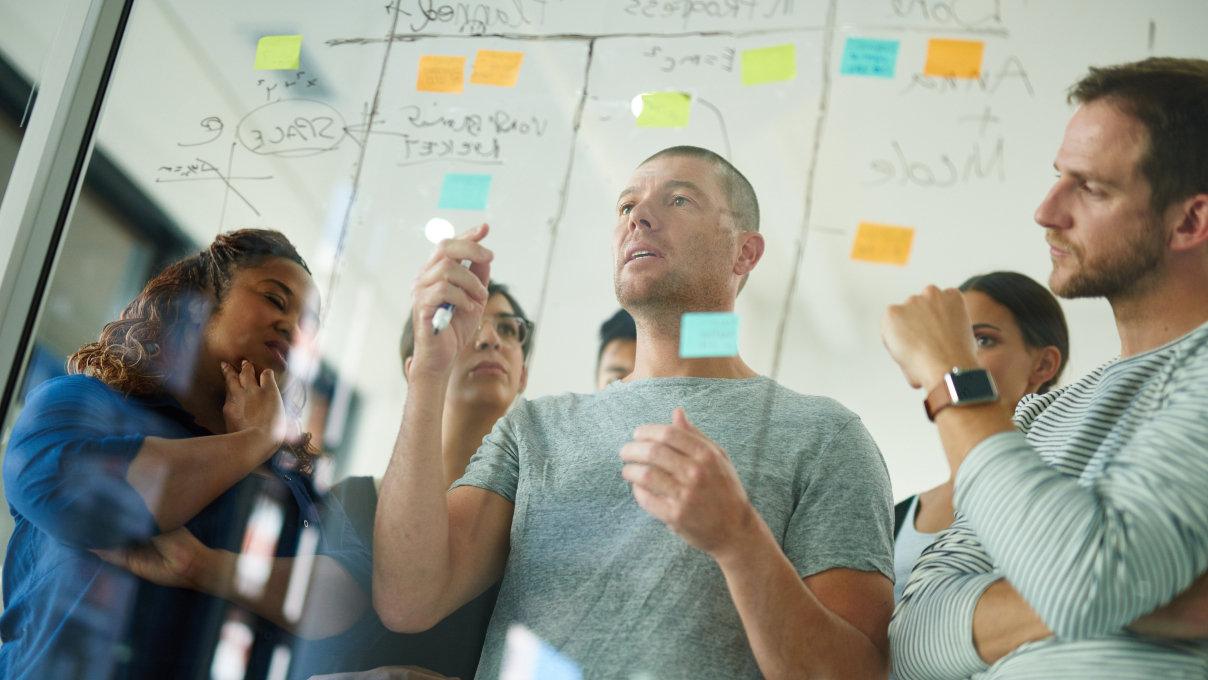
Agile learning is an innovative approach to education and professional development that centers around adaptability, responsiveness, and continuous improvement. It diverges significantly from traditional learning methods by focusing on a learner-centered model, where the process is iterative and flexible, allowing for quick adjustments based on feedback and changing needs.
Key principles of agile learning include collaboration, self-organization, and a focus on real-world applicability. This approach encourages learners to take an active role in their education, fostering critical thinking, creativity, and the ability to rapidly assimilate new information.
When compared to traditional methods, agile learning stands out for its emphasis on practical skills and adaptability, rather than rote memorization and standardized testing. The benefits of agile learning extend to both individuals and organizations: it equips learners with the skills necessary to thrive in a fast-changing world, enhances engagement and motivation, and promotes a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
For organizations, agile learning leads to a more skilled and adaptable workforce, better prepared to meet the challenges of today’s dynamic business environment.
Definition and Key Principles
- Agile Learning Defined: A learner-centered approach that emphasizes adaptability, responsiveness, and continuous improvement in the learning process.
- Key Principles:
- Collaboration: Encourages group learning and teamwork.
- Self-Organization: Allows learners to have more control over their learning journey.
- Real-World Application: Focuses on practical skills and real-world scenarios.
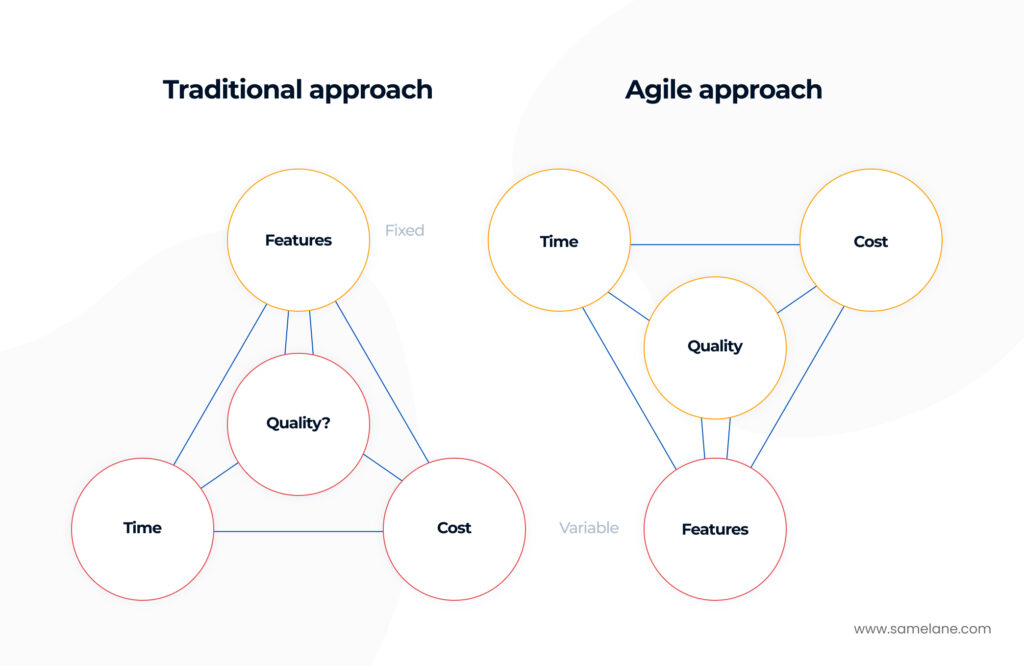
Agile vs. Traditional Methods
- Flexibility: Agile learning adapts quickly to feedback and changing needs, unlike the more rigid traditional methods.
- Learner-Centric: Prioritizes the needs and experiences of the learner, fostering a more engaging and effective learning environment.
- Iterative Process: Emphasizes continuous learning and development rather than a one-time knowledge acquisition.
Benefits of Agile Learning Culture
- For Individuals:
- Enhances critical thinking and creativity.
- Prepares learners for a rapidly changing world.
- Boosts engagement and motivation through active participation.
- For Organizations:
- Creates a workforce that is skilled, adaptable, and innovative.
- Promotes a culture of continuous learning and improvement.
- Improves organizational agility and responsiveness to market changes.
Agile learning isn’t just a methodology; it’s a mindset that prepares individuals and organizations for the challenges of a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape.
Agile Learning Process: Step-by-Step
Transitioning to agile learning involves several key steps, each contributing to the development of a more adaptable and responsive learning environment:
Step 1: Embracing a Flexible Mindset
- Overcoming Resistance to Change: Cultivate an openness to new methods and ideas. This includes letting go of old habits and traditional ways of thinking.
- Encouraging Curiosity and Experimentation: Foster a culture where questioning, exploring, and trying new approaches are valued and encouraged.
Step 2: Adopting Agile Principles
- Understanding Iterative Development: Learn how to build upon knowledge incrementally, making improvements as you go along.
- Emphasizing Collaboration and Feedback: Encourage teamwork and open communication. Feedback should be seen as a valuable tool for growth and improvement.
Step 3: Implementing Agile Learning Culture
- Incorporating Agile Methods: Apply agile techniques such as scrum or kanban in learning or training environments.
- Agile Learning Tools and Resources: Utilize various resources, like collaborative software, online platforms, and interactive learning modules that support agile learning.
Step 4: Measuring and Adapting
- Setting Goals and Benchmarks: Establish clear, achievable objectives for your agile learning initiatives.
- Using Feedback to Refine Processes: Regularly gather and analyze feedback to continuously refine and improve the learning process.
This guide offers a roadmap for individuals and organizations looking to shift towards a more flexible, collaborative, and iterative approach to learning. By following these steps, learners and educators can harness agile learning methodologies’ full potential.

Challenges and Solutions in Agile Learning
Adopting agile learning comes with its unique set of challenges, but with the right strategies, these obstacles can be effectively overcome:
Resistance to Change:
- Challenge: Inertia from traditional learning methods can make shifting to agile approaches difficult.
- Solution: Foster a culture of open-mindedness and continuous learning. Highlight the benefits of agile learning to gain buy-in from stakeholders.
Lack of Familiarity with Agile Methods:
- Challenge: Educators and learners may need to become more familiar with agile principles and practices.
- Solution: Provide comprehensive training and resources. Start with basic concepts and gradually introduce more complex elements of agile learning.
Adapting to a More Collaborative Approach:
- Challenge: Transitioning from a teacher-centered to a learner-centered model can be challenging for educators and students.
- Solution: Encourage collaboration through group projects and discussions. Create an environment where feedback is valued and shared openly.
Balancing Flexibility and Structure:
- Challenge: Finding the right balance between being adaptable and maintaining some level of structure.
- Solution: Set clear goals and guidelines but remain open to adjustments. Use agile tools and techniques to monitor progress and make changes as needed.
Measuring and Assessing Progress:
- Challenge: Traditional assessment methods may need to align better with the agile approach.
- Solution: Implement alternative assessment strategies focusing on practical skills and continuous improvement. Use regular feedback sessions and self-assessments.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, educators, and learners can more effectively embrace the agile learning paradigm, leading to a more dynamic and responsive educational experience.
The Future of Learning: Embracing Agility
As we venture into the future, the landscape of learning and education is poised to undergo significant transformations driven by the need for agility and adaptability:
Increased Emphasis on Adaptive Learning Models:
Future learning environments will prioritize adaptability, using agile models that can quickly pivot based on learner feedback and evolving educational needs. This will enable more personalized learning experiences, catering to individual learning styles and paces.
Lifelong Learning as the New Norm:
The concept of learning as a continuous, lifelong journey will become more prevalent. With the rapid evolution of industries and technologies, staying updated with new knowledge and skills will be crucial for personal and professional growth.
Integration of Technology and Learning:
Cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence and Virtual and Augmented Reality will play a pivotal role in education, offering immersive and interactive learning experiences. These technologies will make learning more engaging and accessible to diverse populations, breaking down traditional barriers.
Focus on Soft Skills and Emotional Intelligence:
As automation and artificial intelligence take over more routine tasks, the human workforce will need to excel in areas machines cannot, such as creativity, critical thinking, empathy, and emotional intelligence. Educational systems will increasingly emphasize these soft skills, recognizing their importance in a technology-driven world.
Collaboration Across Borders:
The future of learning will be characterized by its global nature. Virtual platforms will facilitate collaboration across continents, allowing learners from different cultures to share perspectives and solve problems, fostering a more interconnected world.
Responsive Education Systems:
Education systems must be agile, adapting quickly to the latest scientific discoveries, technological advancements, and societal changes. This will involve updating curricula more frequently and rethinking teaching methodologies to prioritize critical thinking over rote memorization.
Emphasis on Sustainable and Ethical Learning:
With growing awareness of global issues like climate change and social inequality, there will be a greater emphasis on sustainability and ethics within education. Learning will not only be about personal or economic success but also about contributing positively to the world.
Decentralization of Education:
The future will likely see a decentralization of education, moving away from traditional institution-centered models to diverse learning platforms, including online courses, experiential learning, and community-based education. This shift will democratize learning, making it more accessible and varied.
In this rapidly changing world, agility in learning isn’t just an asset; it’s a necessity. The future of education, focusing on adaptability, lifelong learning, and global collaboration, promises to prepare individuals not just for the workforce but for a more interconnected and complex world.

Conclusion
In summary, the transition from conventional to agile learning is a pivotal move in the evolving education and professional development landscape. With its emphasis on adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement, Agile learning stands in contrast to traditional, rigid learning methodologies. It offers a more dynamic and responsive approach well-suited to the demands of our rapidly changing world.
Key Points:
- Agile Learning vs. Traditional Methods: Agile learning differs from traditional methods by being more learner-centered, flexible, and responsive to change.
- Benefits of Agile Learning: This approach offers numerous advantages, including enhanced creativity, critical thinking, and a better alignment with real-world scenarios.
- Transition Steps: The transition involves embracing a flexible mindset, adopting agile principles, implementing agile techniques, and continually measuring and adapting learning processes.
- Overcoming Challenges: Challenges such as resistance to change and the need for new assessment methods can be overcome with targeted strategies and a commitment to continuous improvement.
- Future Outlook: The future of learning is agile – emphasizing continuous, lifelong learning, integration of technology, and a focus on soft skills and emotional intelligence.
As we conclude, it’s essential to recognize the significance of this shift towards agile learning. It’s not merely a change in methodology; it’s a transformative approach that prepares individuals and organizations for the challenges of a complex, ever-evolving world. Agile learning equips learners with the skills to adapt, grow, and thrive in diverse environments.
The path towards agile learning may seem daunting to the readers embarking on this journey, but it’s a journey worth taking. It promises enhanced knowledge and skills and a more engaging, relevant, and fulfilling learning experience. Start small, stay open to change, and embrace the principles of agility in your learning endeavors. The future belongs to those prepared to learn, unlearn, and relearn agilely.











