Big Data in HR goes mainstream![1] Such statements can be found in the media about management and HR. Moreover, instead of asking if they should introduce analytics, companies more and more often ask how to do it for the benefit of their business.
If you are interested in the relationship between HR and Big Data – meaning the potential benefits and tools which can be used to develop people analytics in your company – read on!
This article will explain the following:
- What is Big Data and what data can be used with regard to HR?
- What results can be expected from analytics and what benefits can it bring?
- In what areas of HR can big data be introduced?
- What tools can help collect and process data in the field of human resource management?
Big Data and HR
Big Data has been defined by the McKinsey Global Institute as “any set of data that is too large for typical software tools to capture, store, manage and analyze.[2]” The data generated by employees certainly falls within the definition above. It could be, among others, information on recruitment, productivity, training and development, employee satisfaction and commitment.
Possessing data is the primary key factor in introducing Big Data. Another one is the departure from their traditional storage, e.g. paper documentation or even folders of text documents, in favor of specific digital tools. These allow companies to analyze, control, predict and implement solutions leading to better results. Within HR, such data can answer the following questions:
- where to get the most valuable candidates?
- how to keep them?
- how to increase their performance?
The competitive advantage obtained through such analyses is, therefore, invaluable.
Specialists from Nucleus Research set out to analyze this process. Their research leads to the conclusion that one dollar invested in analytics returns three hundred times[3] – although it should be noted that these results were obtained in general business terms. Additionally, talent analytics, a subset of people analytics, has grown in popularity as a result of its ability to offer insightful data on employee productivity, involvement, and retention. Employee costs are frequently the largest fixed expense for many businesses, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize their human resource management, which can result in significant cost savings.
It is also worth adding that human resources specialists very often consider what structural opportunities and benefits their departments can bring and what results are achieved through internal processes. HR analytics allows companies to transfer planning, controlling and management to each of the 4 levels of the organization related to employees.
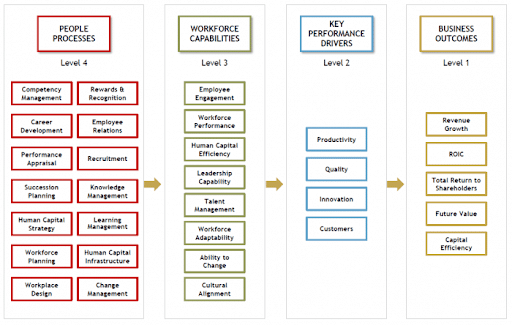
The company Xero, which runs a call center and whose approach to Big Data was described in The Wall Street Journal, may serve as an example here. It used collections of big data to find out why employees stay with the company and to discover the reasons for their departure. Using this information, Xero minimized their dropout rate by 20% during a 6-month trial period.[5] The process concerned as many as 48,700 employees, so the result can definitely be considered a success.
What data is crucial for HR and the entire organization?
Human resource management provides a lot of information which has the potential to draw interesting conclusions using Big Data. Examples include the following areas and particular examples of data worth attention:
Recruitment
There are a lot of recruitment measures. The most important ones should include the sources of candidate acquisition, application conversion, time per hire, time at each recruitment stage or the time needed to reject a candidate, candidate drop-off rate, salary analysis, task results, and competency tests.
Learning & Development
In this respect, it is possible to monitor such data as ongoing and completed training courses, the time needed for the achievement of results, and the timelines of the processes. The effectiveness of courses can be compared, as well as test results achieved individually or in departments. Competency profiles and self-development progress can also be tracked.
Employee performance
Here, you can gather information, from goal achievement, through career progress, to supervisor feedback and 360 feedback. It is beneficial to add information about shifting career paths and changing payroll, as well as data on income per employee, personnel retention and relationships with the manager. These aspects can also be combined with the employee activity, which indicates motivation and commitment, e.g. participation in company events, results from satisfaction surveys and employee interviews. These elements also have a direct impact on employee retention.
Future Casting
In this area, information such as external competition and market analysis can be gathered, including: wage bench-marking, social media activity, company competitiveness, employer branding activities (e.g. speeches at conferences or promotional campaigns). All this, together with global trends, means that business analytics can be used to predict the future including some external conditions, which may in turn translate into specific recommendations.
Using data to improve the businesses
Given the above-mentioned data, a series of analyzes can be performed. Specialists use the following:
- descriptive analysis – including volumes, cuts or costs;
- interconnection analysis – providing insight into performance in relation to the requirements or standards (for example, the percentage of implementation of specific provisions to which the company is obliged);
- result analysis – showing the relationship between activities and results (e.g. the quality of new hires and rotation in the first year of employment)
- predictive analytics – to determine the statistical relationship between actions and outcomes and to forecast what may happen in the future.
Analyzing and monitoring is a means to evaluate the current situation, while reporting leads to conclusions for the future. This, in turn, translates into the possibility of influencing performance and constantly improving results. Each of the above-mentioned areas – from recruitment, through learning & development or performance management, to future casting, can undergo a diagnosis which allows the company to define the pros and cons of the processes. As a result, solutions can be tested, results can be compared and, finally, satisfactory outcomes can be achieved at all levels.
How to start using analytics and Big Data? What tools can help?
The road to corporate culture and data-driven management is long and often perceived by employees as soulless. That is why starting with small steps is advisable. It is best to begin with areas which are not connected with employee performance, because this is where the greatest opposition most often appears. Areas such as e-learning or recruitment are a popular choice, making it easier for employees to perform their duties. Below, we provide 4 examples of product classes which help process Big Data in daily operations.
- ATS (Applicant Tracking System) is a recruitment system that collects all data related to this area. It tracks the efficiency of sources, employee conversion, and all the data related to time and activity in the system. Recruitee, GreenHouse or Workable may serve as good examples of this kind of solution. They provide in-depth analyses of the processed data.
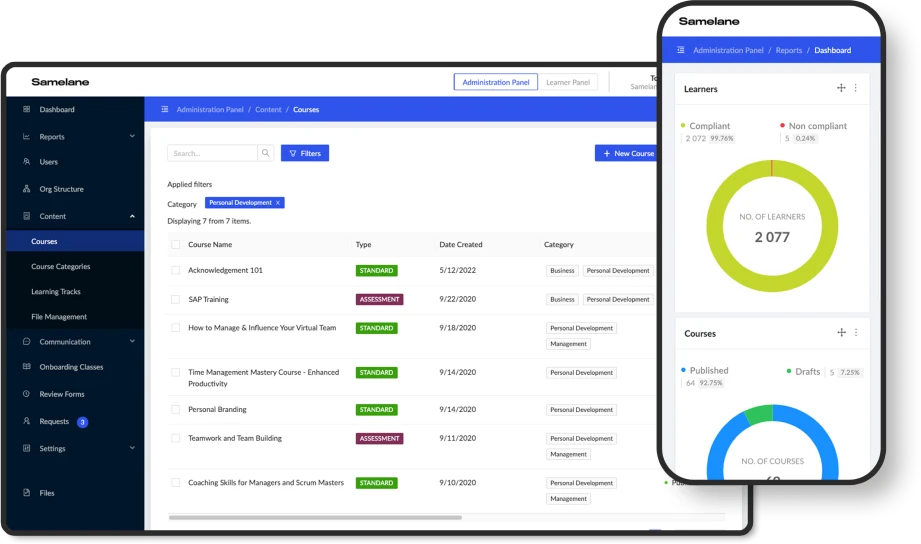
- LMS stands for a learning management system. An LMS is often used as an e-learning platform expanded with functionalities granting appropriate access. It is also equipped with analytical modules. They track the progress of employees, but also the popularity of individual content. Additionally, successes are measured and certificates are awarded. Progress made over time, in addition to facilitating the daily operations, can interest employees and make e-learning a challenge for them instead of an obligation. Samelane is an example of this type of platform.
- HRMS / HRIS (HR Management System / HR Information System) are classes of applications which manage human resources and processes related to the employee life cycle. Important modules are related to HR issues – employee documentation, working time management, wages, taxes, benefits and other settlements. In addition, modern solutions are sometimes extended by, for example, onboarding support or an employee communication platform. Hi Bob is an interesting example of this type of solution.
- Performance Management System (PMS) – is a solution which often worries employees the most. It allows management to monitor staff performance and results in the context of defined goals. At the same time, it can directly translate into defining goals and achieving better results.
Big Data offers a wide spectrum of possible improvements which can be implemented in any company – both in terms of organization, efficiency, but also employee commitment and motivation. Discovering trends, strengthening positive aspects and eliminating hiccups limiting productivity are essential for success. It is worth remembering that technology will never replace the human element of HR. The use of dedicated systems allows companies to collect and manage data. However, qualitative data and the situational context, along with an individual approach lead to better decisions. The combination of these factors results in risk reduction and effective employee management.










